Gluten-Free Diets and Coeliac Disease
Gluten-free diets are an option for people with coeliac disease. This disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, a substance found in wheat, barley, rye, and oats. Taking out gluten from your diet can greatly reduce symptoms. One skin manifestation of coeliac disease is called dermatitis herpetiformis (DH). DH causes red, raised patches of skin that are usually covered in blisters. This condition affects one in every 3,300 people.
What are the early warning signs of celiac disease
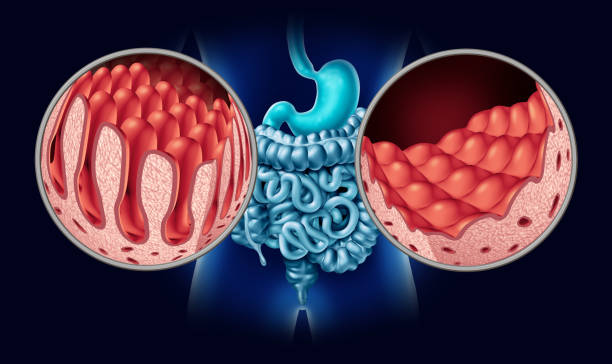
There are a variety of tests that can help diagnose coeliac disease. Blood tests can check for abnormalities in the blood, including high levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and antibodies to gluten. An endoscope, or thin, hollow tube, can also be used to examine the small intestine. This test can reveal damage to the villi.
Diarrhea is another common symptom. This is the result of damaged villi, finger-like projections that help the small intestine absorb nutrients. Diarrhea can also be a symptom of malabsorption, when the lining of the intestines cannot absorb nutrients properly. Other symptoms include changes in poop color, including pale poop that is fatter than normal.
What causes coeliac disease?
Coeliac disease is a multifactorial autoimmune disorder. It’s caused by changes in genes, most notably in the HLA-DQ genes. These genes are important for the development of the immune system, and people with mutations in these genes are at a higher risk of developing coeliac disease. About one third of the population is affected by a mutation in one or more of these genes. Because of this, it is important to understand how these changes lead to coeliac disease.
People with coeliac disease may experience problems with their digestive system. In some cases, this can lead to severe malnutrition. The body cannot absorb the proper amounts of nutrients, which can lead to a variety of health problems, such as a lack of energy, muscle wasting, and fatigue. In children, malnutrition can delay puberty and prevent normal growth. The most effective treatment for coeliac disease is to increase the amount of food you eat and to take supplements.
Is Coeliac a serious disease?
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system reacts abnormally to gluten, a protein found in wheat. It damages the lining of the small intestine and prevents it from absorbing essential nutrients. Although it has no known cure, the disease can be controlled by a gluten-free diet. A gluten-free diet can help patients maintain a nutritious diet, even without the need for medication.
Symptoms of coeliac disease include anaemia, abdominal pains, and wind. However, most of these symptoms subside after several months on a gluten-free diet. Other symptoms include diarrhea, mouth ulcers, and bloating. Those who suffer from coeliac disease may also develop an anxiety disorder or develop a blistering skin condition.
Can celiac go away?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for celiac disease, although a gluten-free diet can help manage the symptoms. The diet also helps the body heal from the damage caused by gluten. A gluten-free diet is a lifelong requirement for patients with the disease. However, it is important to keep in mind that the disease can recur if left untreated.
In order to determine whether a patient has celiac disease, they will have to undergo a serological test to check for antibodies against gluten. This test is more sensitive for IgA antibodies than it is for IgG antibodies. Symptoms of celiac disease include fatigue, nausea, and bloating. Some people will also experience skin rashes. In some cases, the symptoms will occur just a few hours after consuming gluten.