How to Treat Jungle Rot Disease
If you’ve recently learned that you have jungle rot, you’re probably wondering what to do to treat it. Fortunately, jungle rot is treatable with the right treatment. There are a few different ways you can treat jungle rot, including using broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as ampicillin and tetracycline. But penicillin alone is not likely to cure the disease, so talk to your doctor to find the right treatment regimen. And it’s important to take the antibiotics for the full course recommended by your doctor. Otherwise, jungle rot could return or get worse.
Treatments
Although jungle rot disease is extremely contagious, there are several simple treatments for it. The first step is to wash the affected area thoroughly. This will help reduce the spread of the disease and promote healing. Antibiotics can also help. Broad-spectrum antibiotics such as tetracycline, ampicillin, and mebendazole are effective against jungle rot. Sometimes, a single dose of penicillin is enough to treat the condition. However, if the infection does not respond to penicillin, you may need to take additional antibiotics. Remember to finish all prescribed antibiotics and to consult your doctor to determine the most effective treatment.
The Veteran was diagnosed with jungle rot disease during his deployment to Guam. The condition usually flares up in summer months. His medical records showed that the rash often reached up to his knees, and was worse in hot weather. In addition, he used topical steroids to treat the rash. His symptoms were accompanied by itching, burning, flaking, and scaling.
The treatment for jungle rot disease depends on the severity of the disease. In severe cases, amputation may be necessary. If the disease is not properly treated, it can return later and worsen. In severe cases, debridement may be required under local anesthesia. This procedure removes unhealthy tissue from the affected area and promotes healthy tissue growth. Sometimes, debridement can save a healthy limb from amputation.
Symptoms
The bacterial infection that causes jungle rot disease is widespread in hot, tropical climates. Most of Africa and South America are affected, as are India, Pakistan, and Iran. The disease can also be found in Southeast Asia, and is best treated with antibiotics. Initially, it is treated with penicillin, and later with broad spectrum antibiotics. In severe cases, the patient may require skin grafting. The disease can also affect the bones and muscles. In the most severe cases, surgery is necessary.
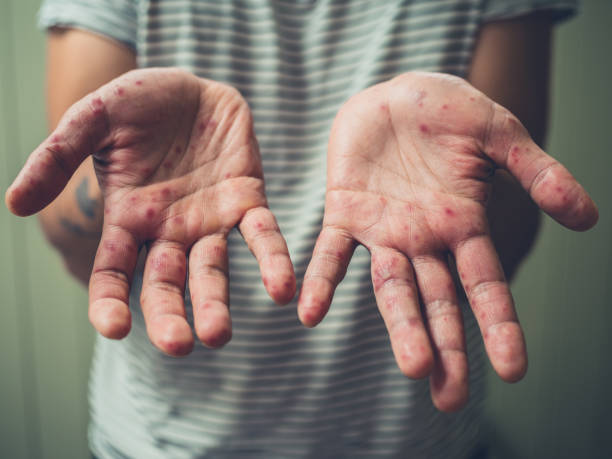
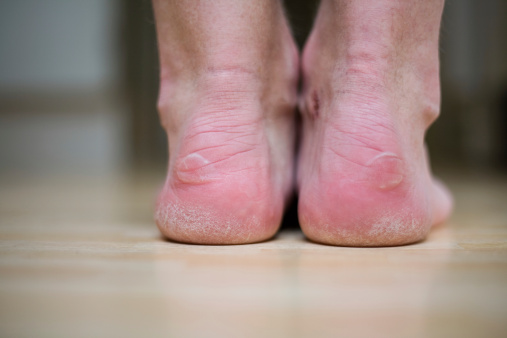
The size of a jungle rot ulcer varies from half an inch to thirteen inches in diameter, depending on the extent of the infection and the person’s overall health. The disease is typically less serious in healthy individuals than in sicker ones, but it can be very painful. The ulcers can spread to the bones if not treated early. To treat jungle rot ulcers, the affected areas must be kept clean. In addition, they must be bandaged to ease the pain. Non-adhesive dressings should be used. It is also recommended that the affected areas be kept dry at all times.
The Veteran is suffering from a skin disorder that began during his service. However, there is no medical evidence to prove that jungle rot was the cause of his symptoms. He has been treated nine or ten times for this condition. He is now on a no-duty status and claims that jungle rot caused him to have cracked, bleeding feet.
Causes
Jungle rot disease is a bacterial infection that affects the skin and tendons. In severe cases, it can spread to the bones and muscles. While there is no specific cure for jungle rot, it can be easily managed with proper care and treatment. In some severe cases, treatment may include amputation.
The infection is caused by a variety of factors, including prolonged exposure to damp conditions. In its most common form, jungle rot is caused by excessive exposure to water at temperatures higher than 20 degrees. It can be transmitted from person to person by sharing shoes or floors. This is why wearing clean shoes and socks is essential. Wearing pants that extend to the ankle can also help reduce the risk of developing the infection.
Good water management can also reduce the risk of Phytophthora rot. Proper water management helps reduce the amount of water in the soil around susceptible plants. It is also important to monitor soil moisture levels around trees. Proper irrigation should be conducted only when it is needed. Orchard owners should use low-angle sprinkler heads to avoid wetting the lower branches. Also, a drip system should be installed with emitters positioned a foot away from the trunk.
Foot rot can be caused by various environmental factors. Continuous exposure to wet conditions, including muddy soil, can cause the infection to spread. In addition to moist environments, foot rot may be caused by mechanical damage or injury. Infections caused by foot rot can affect the whole body, including the intestines.
Prevention
There are many ways to prevent jungle rot disease from infecting you. The first is to make sure you are wearing the appropriate clothing and shoes. This is especially important if you work in an area with mud or standing water. You also need to keep your feet clean and dry. This is important because moist environment is conducive to the growth of bacteria. Using a product like Tinactin, which is available over the counter, can help keep your feet dry. It is also important to wear breathable shoes.
One of the most important ways to prevent jungle rot is to wash your feet often. Infected feet can develop a scaly, red, and itchy rash that can be painful. The skin may also crack and flake. It can also lead to open sores.
Another way to prevent jungle rot is to use good water management. You want to avoid prolonged soil saturation that will lead to standing water around your trees and other susceptible plants. If you must use irrigation, make sure you irrigate only when necessary. You also want to monitor soil moisture around your trees and make sure you don’t wet the lower branches. Another good way to avoid wetting the trunk is to use splitters and sprinkler heads that are low-angled. In addition, the emitters of drip systems should be at least a foot away from the trunk and planted in shallow soil.
Tea tree oil
Tea tree oil is an all-natural remedy for jungle rot disease that is widely available. It is an effective disinfectant and anti-parasitic. You can purchase the oil at health food stores or online. However, there are some important things to consider when using it. First, tea tree oil can irritate the skin and should be diluted with a carrier oil. In addition, it should never be taken internally.
Tea tree oil has antifungal properties and can prevent the growth of fungi on foliage. It can also repel whiteflies that produce sticky dew that feeds sooty mold fungi. However, you should not use tea tree oil for this purpose if you have allergies or are sensitive to its smell.
If you’re concerned about the safety of tea tree oil for jungle rot disease, try mixing it with a carrier oil that’s soothing for your horse. Coconut oil, aloe vera, or other oils can be used as well. All of these essential oils contain antibacterial properties and can help alleviate Rain Rot. You can also try Equi-Spa’s The Balm, which contains many essential oils and can treat all types of skin problems.
A double-blind study comparing tea tree oil to a prescription antifungal drug showed that tea tree oil is as effective as clotrimazole. In the trial, 117 patients were randomly assigned to either tea tree oil or clotrimazole. Compared to the placebo group, tea tree oil was a better treatment for the majority of people.
Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease that is transmitted to humans by sandflies. In most cases, the disease is fatal. It causes weight loss, irregular fever, enlargement of the spleen, and anemia, among other symptoms. Most cases are found in India, Brazil, and East Africa, with an estimated 50 000 to 90 000 new cases reported annually. While only 25 to 45 percent of these cases are reported to the World Health Organization (WHO), this disease remains one of the most prevalent parasitic diseases with outbreaks.
Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by parasitic one-celled organisms, called protozoa. They infect humans and other animals through the bite of certain species of sand flies. Symptoms of this disease include sores on the skin, which progress to ulcers, and fever, and may eventually lead to an enlarged liver and spleen. The disease was virtually unknown in Asia prior to WWII, but it is now a global health issue.
The disease is usually treated with antibiotics. Penicillin is effective in the early stages and broad spectrum antibiotics are effective in later stages. A non-adherent dressing is necessary for the treatment of the infection. In severe cases, skin grafting may be required. Large ulcers may require debridement under anesthesia. In some cases, amputation may be necessary. Prevention of the disease is key to reducing the risks of further complications.
Leishmaniasis is caused by protozoan parasites. They are transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female phlebotomine sandflies. Despite its prevalence, it is not spread by terrorists.